Curriculum and Credit Framework for UG Programme: A New Road Map for Flexible Learning
In this competitive world, nations are heading towards more advanced and refined ways to enhance the skills and knowledge of their students and build a strong new generation of professional forces. In this race, India’s core education body, the University Grants Commission, and its expert committee have drafted the Curriculum and Credit Framework for Undergraduate Programme. The ideation was acknowledged in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which stated that higher education is crucial to advancing both individual and societal well-being. As a result, we require high-quality higher education that aims to develop thoughtful, well-rounded, creative, and unique individuals with specialized knowledge in a variety of disciplines, such as the sciences, social sciences, arts, humanities, languages, and professional, technical, and vocational subjects.

Among the several changes in the education framework, UGC has formulated a more student-centric “Curriculum and Credit Framework for Undergraduate Programmes (CCFUP)” that builds on a flexible choice-based credit system, a multidisciplinary approach, and multiple entry and exit options. credit transfer, equivalence, etc.
Apart from flexibility in switching disciplines and easy entry and exit, the main feature of the new curriculum is the adoption of flexibility for learners to move from one institution to another to enable them to have multi-interdisciplinary learning and switch to alternative modes of learning (offline, ODL, and online learning, and hybrid modes of learning).
The new framework will help in preparing professionals in cutting-edge areas such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), 3-D machining, big data analysis, and machine learning, in addition to genomic studies, biotechnology, nanotechnology, neuroscience, with important applications to health, environment, and sustainable living that will be woven into undergraduate education for enhancing the employability of the youth.

Minimum Credit Awards for UG Diploma, Degree and Certificate
Now comes the crux of the curriculum framework, which is to provide minimum credits to award an UG certificate, diploma, and degree. Prior to that, UGC defined major and minor disciplines, as the major discipline is the main focus and students earn 50% of their total credits through it. A minor discipline broadens a student’s understanding beyond the major discipline.
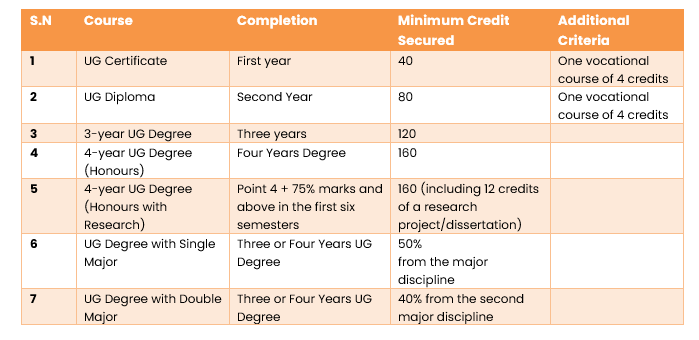
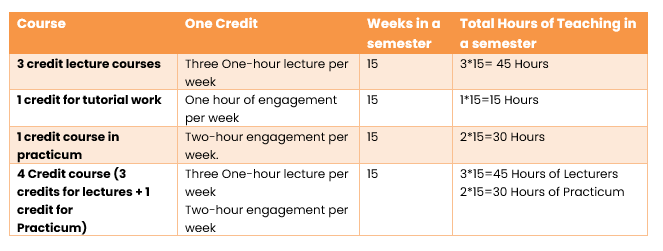
The important point in understanding the entire curriculum framework is the distribution of credit hours for different types of courses. UGC has defined the credit hours as a workload during the course, and it is considered a unit of measurement of the course that determines the number of hours of instruction required per week over the duration of a semester (at least 15 weeks).
Each course may have a lecture component, a blend of lecture and tutorial components, a lecture and practicum component, a lecture, tutorial, and practicum component, or only a practicum component. Let’s understand through some examples.
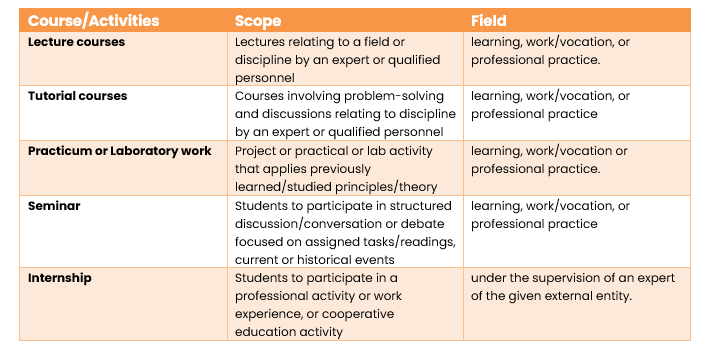
Programme Of Study
The framework has also broadened the scope of the different types of activities or courses to consider in the programme of study.
The goal of the new curriculum framework is to give students the freedom to choose courses from various branches of UG courses. This requires that all departments prescribe a certain specified number of credits for each course and common instruction hours also known as Slot time. UGC kept its options open to HEIs to decide a credit course and distribution across six or eight semesters, but it has suggested the number of credits per course and the credit distribution that will facilitate the students’ meeting the minimum credit requirements.
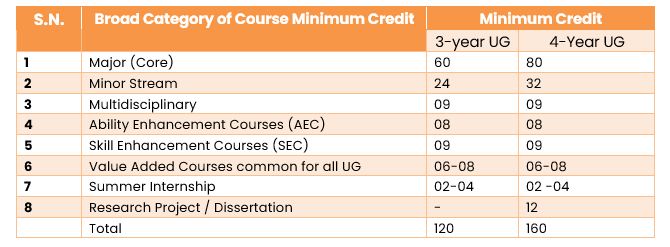
The curriculum consists of major stream courses, minor stream courses, and courses from other disciplines, which are natural and physical science, mathematics, computer applications, etc.; ability enhancement courses; skill enhancement courses; and value-added courses common to all UG, which include environmental education, understanding India, digital and technological solutions, health and wellness, yoga education, and sports and fitness. At the end of the second semester, students can decide whether to continue with the chosen major or request a change of major. The minor stream courses include vocational courses, which will help the students equip themselves with job-oriented skills.
Level of Course and Credit Score
UGC credits the curriculum framework for enhancing learning outcomes based on the levels of courses. In order to get the degree, diploma, and certificate, students will now have to get minimum credit based on the level of course they opt for. This will transform UG education from traditional knowledge to more practical and skill-based learning.
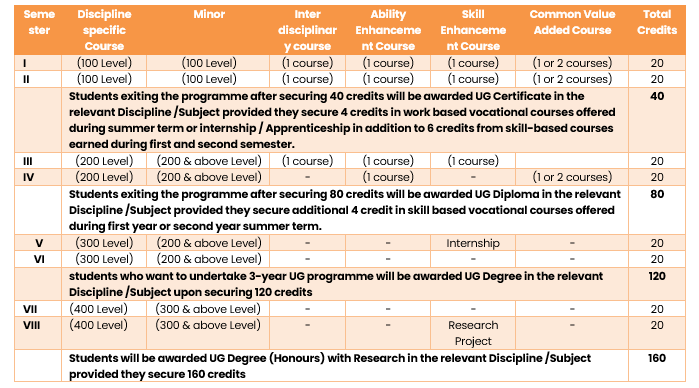
Using Learning Outcomes in order to effectively create and implement curricula, pedagogical strategies must be focused on helping students achieve the specified learning outcomes for the course they opt for. The outcome-based approach necessitates a considerable transition from teacher-centric to learner-centric and enhances the overall learning experience with more practical understanding and know-how.
Since the new UGC UG credit curriculum framework provides a highly advanced manner to improve learning quality, build skills, and prepare students for the workforce with a wide range of skill sets and knowledge, it will be extensively embraced by higher education institutions.